I’ve been
shocked by the extent and persistence of UK inflation over the past
few months, together with many others. So what did I get incorrect?
Why is UK
inflation so persistent?
Let’s begin by
searching for clues. The largest is that inflation is proving extra of a
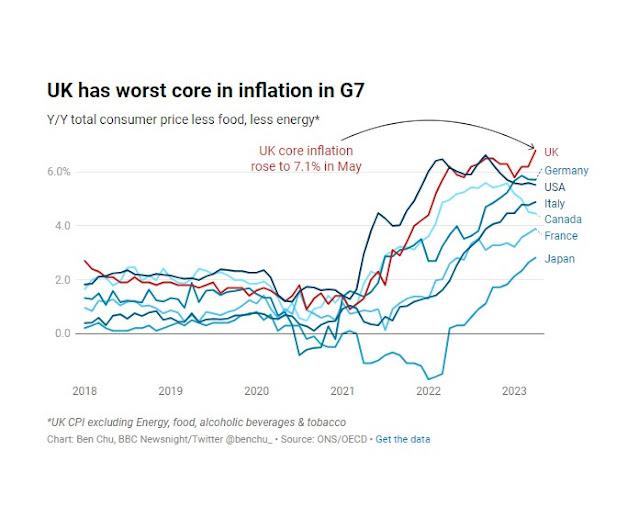
downside within the UK than elsewhere. Listed here are a few charts from
Newsnight’s Ben Chu. The UK has the worst headline
inflation within the G7
and the worst core
inflation (excluding vitality)
That Brexit would
make Inflation worse within the UK than different international locations isn’t a
shock. I talked
about this over a yr in the past, though again then US core
inflation was greater than within the UK. In that publish I listed numerous
explanation why Brexit may elevate UK inflation (see additionally right here).
Might a few of these additionally account for its persistence?
The one most
generally cited is labour shortages caused by ending free
motion. Right here is the newest breakdown of earnings
inflation by broad trade class.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Across the center of
final yr the labour shortage story was clear within the knowledge. One key
space the place there was a persistent scarcity of labour was in resorts and
eating places, and wage development in that sector was main the way in which.
Nonetheless if we have a look at the newest knowledge, that’s now not the
case, and it’s finance and enterprise companies the place earnings development
is strongest. This dovetails with a fall in vacancies within the
wholesale,retail, resorts and restaurant sectors for the reason that summer time of
final yr (though the extent of vacancies stays above end-2019
ranges). Has there been a current enhance in vacancies in finance and
enterprise companies? No, the reason for top earnings development in
that sector lies elsewhere.
Earlier than coming to
that, it’s price noting that any earnings development numbers above 3-4%
are inconsistent with the Financial institution’s inflation goal, and the labour
market does stay tight, though not as tight as a yr in the past. One
partial clarification for UK inflation persistence is that it displays
the implications of persistently excessive (in extra of 3-4%) wage
inflation, which in flip displays a good labour market.
UK worth inflation
is now not only a consequence of excessive vitality and meals costs, as
this breakdown makes clear.
Whereas vitality and
meals costs are nonetheless greater than common inflation, probably the most
worrying line from the Financial institution’s perspective is the inexperienced one for inflation in all companies. It’s
this class the place inflation is (slowly) rising, and the newest
charge of seven.4% is the principle motive why UK inflation seems to be so
persistent. It’s now not the case that UK inflation is being
generated by exterior elements that can not be influenced by the Financial institution
of England. That can be why it may be a bit deceptive to speak about
inflation persistence or sticky inflation, as a result of the costs that
are going up now usually are not the identical as had been going up only a yr in the past.
This excessive degree of
companies inflation could possibly be a response to excessive nominal earnings
development, with maybe nonetheless some lagged impact from greater vitality
prices [1], however current knowledge for earnings suggests a 3rd issue
concerned. Right here is the share of the working surplus for firms
(i.e. company earnings) to GDP since 1997.
UK
Revenue Share
Other than a spike
within the first quarter of the pandemic, this measure of the revenue
share has stayed beneath 24% since 2000, averaging about 22% between
2000 and 2022. Nonetheless the top of 2022 noticed this share rise to 22.5%,
and the primary quarter of this yr noticed an enormous enhance to 24.7%.
Now we have to watch out right here, as this sudden enhance within the revenue
share could possibly be revised away as higher knowledge turns into out there. But when
it isn’t, then it seems as if among the current persistence is
coming from corporations rising their revenue margins.
Why may corporations be
rising their revenue margins? This won’t be sudden throughout
a interval the place client demand was very buoyant, however with the price of
residing disaster that isn’t taking place. It could be that corporations have
determined that an inflationary atmosphere offers them cowl to lift
revenue margins, one thing that appears to have occurred within the US and EU. Nonetheless one other issue is Brexit as soon as once more. EU
corporations now face greater prices in exporting to the UK, and this may occasionally
both cause them to withdraw from the UK market altogether, or to attempt
and get better these prices by way of greater costs. Both means that permits
UK corporations competing with EU corporations within the UK market to lift their
costs. In the event you have a look at what I wrote
a yr in the past, that impact is there too, but it surely was
unattainable to understand how giant it could be.
What’s to be
carried out?
The mainstream
consensus reply is to make use of rates of interest to maintain demand subdued to
guarantee wage and domestically generated worth inflation begin coming
down. It doesn’t matter if the inflation is coming from earnings or
earnings, as a result of the treatment is identical. Lowering the demand for labour
ought to discourage excessive nominal wage will increase, and lowering the
demand for items ought to discourage corporations from elevating revenue margins.
On this context, the controversy about whether or not employees or corporations are
chargeable for present inflation is inappropriate.
That doesn’t
essentially indicate the Financial Coverage Committee of the Financial institution was proper
to lift rates of interest to five% final week. Certainly two educational
economists on the MPC (Swati Dhingra and Silvana Tenreyro) took a
minority view that charges ought to keep at 4.5%. I most likely would have
taken that minority view myself if I had been on the committee. The
key challenge is how a lot of the influence of earlier will increase has but to
come by way of. As I word beneath, the present construction of mortgages is
one motive why that influence could take a while to fully emerge.
That demand has to
be diminished to carry inflation down is the consensus view, and it’s
additionally for my part the proper view. There may be at all times a query of
whether or not fiscal coverage must be doing a few of that work alongside
greater rates of interest, but it surely already is, with taxes rising and
spending cuts deliberate for the longer term. Rising taxes additional on the
rich is a good suggestion, but it surely doesn’t assist a lot with inflation,
as a result of a big proportion of excessive incomes are saved. An argument I
don’t purchase is that greater rates of interest are ineffective at lowering
demand and due to this fact inflation. The proof from the previous clearly
reveals it’s efficient.
For anybody who says
we should always low cost the proof from the previous on how greater curiosity
charges scale back demand as a result of the world is totally different right this moment, simply suppose
about mortgages. Due to greater home costs, the revenue lack of a
1% rise in rates of interest is bigger now than it was within the 70s or
80s. But as a result of many extra persons are on briefly fastened charge
mortgages, the lag earlier than that revenue impact is felt is far higher,
which is a vital argument for ready to see what the influence of
greater charges might be earlier than elevating them additional (see above). There
is nevertheless one space the place the federal government can intervene to enhance the
pace at which greater rates of interest scale back inflation, which I’ll
discuss beneath.
With the economic system
nonetheless struggling to regain ranges of GDP per capita seen earlier than the
pandemic [2], it’s fairly pure to dislike the concept coverage
must be serving to to cut back it additional. This sadly results in a
lot of wishful considering, on each the left and the appropriate. For some on
the left the reply is worth controls. The foremost downside with worth
controls is that they deal with the symptom slightly than the trigger, in order
quickly as controls finish you get the inflation that was being repressed.
As well as they intervene with relative worth actions. They’re
not a long run resolution to inflation.
Sunak on the
starting of the yr made a deceitful and now silly pledge to half
inflation. It was deceitful as a result of it’s the Financial institution’s job to regulate
inflation, not his, so he was attempting to take the credit score for somebody
else’s actions. It has grow to be silly as a result of there’s a good
probability his pledge won’t be met, and there’s little he can do
about it. When challenged about making pledges about issues which have
little to do with him he talks about public sector pay, however this has
nothing to do with present inflation (see postscript
to this)! As I famous
final week, the Johnsonian behavior of mendacity or speaking
nonsense in public lives on beneath Sunak.
The thought amongst
Conservative MPs that mortgage holders ought to by some means be compensated
by the federal government for the influence of upper rates of interest can be
wishful considering on their half, reflecting the prospect of those MPs
dropping their seats. Whereas there’s each motive to make sure lenders do
the whole lot they will for debtors who get into critical difficulties,
to nullify the revenue impact of upper mortgage charges can be to
invite the Financial institution to lift charges nonetheless additional. [3] Sunak can not each
assist the Financial institution in getting inflation down and on the similar time attempt
and undo their technique of doing so. As well as there are different teams
who’re in additional want of safety from the influence of inflation than
mortgage holders.
One other argument
towards excessive rates of interest is that inflation right this moment displays weak
provide slightly than buoyant demand, so we
ought to attempt to strengthen provide slightly than scale back
demand. Once more this seems like wishful considering. First, demand within the
labour market is kind of sturdy, and there aren’t any clear indicators of above
regular extra capability within the items market. Second, the issues we
have with provide – principally Brexit – usually are not going to be fastened
rapidly. To repeat, it’s the domestically generated inflation slightly
than the exterior worth pressures on vitality and meals that characterize the
present downside for inflation.
An analogous argument
pertains to actual wages. Folks ask how can nominal wage will increase be a
downside, when actual wages are falling and are round
the identical degree as they had been in 2008? A part of the
reply is that, so long as the costs of vitality and meals stay excessive,
actual wages should be decrease. (The concept that earnings alone ought to take
the hit from greater vitality and meals costs is ideological slightly than
sound economics.) As a result of greater vitality and meals costs scale back slightly
than enhance the earnings of most corporations, they’re sure to move on
greater nominal wages as greater costs.
But there’s one new coverage measure that will assist just a bit with the struggle towards
inflation, and so assist reasonable how excessive rates of interest must go.
As I famous earlier, the sector main wage will increase for the time being
is finance and enterprise companies. In finance at the very least, a few of this
might be earnings led due to bonuses or implicit revenue sharing.
Financial institution earnings are rising for numerous causes, certainly one of which is that the
Financial institution of England is paying them extra for the Financial institution Reserves they maintain.
There’s a sound
financial case for taxing these earnings no matter is
taking place to inflation, and the truth that greater taxes on banks may
assist scale back inflationary stress is a bonus proper now.
What did I get
incorrect? Simply how dangerous the state of the UK economic system has grow to be.
Whereas the Financial
Coverage Committee (MPC) of the Financial institution of England could have underestimated
the persistence of UK inflation, I’ve for a while been arguing
that the Financial institution has been too hawkish. On that, MPC members have been
proved proper and I’ve been incorrect, so it is necessary for me to work
out why.
a part of that
has been to underestimate how resilient the UK economic system has thus far
been to the mixture of upper rates of interest and the price of
residing disaster. I assumed there was a great probability the UK can be in
recession proper now, and that in consequence inflation can be falling
way more quickly than it’s. Evidently a lot of those that constructed
up financial savings throughout the pandemic have chosen (and been in a position) to cushion
the influence of decrease incomes on their spending.
However flat lining GDP,
whereas higher than a recession, is hardly something to jot down house
about. As I famous above, UK GDP per capita has but to regain ranges
reached in 2018, not to mention earlier than the pandemic. If the UK economic system
actually is ‘working too scorching’ regardless of this comparatively weak restoration
from the pandemic, it could indicate the relative efficiency of the UK
economic system since Brexit specifically (however ranging from the International
Monetary Disaster) was even worse than it appeared
simply over a yr in the past. If I’m being actually trustworthy, I
didn’t wish to consider issues had grow to be that dangerous.
This hyperlinks in with
evaluation by John Springford that means the price of Brexit thus far
when it comes to misplaced GDP could also be an enormous 5%, which is at
the upper finish (if not above) what economists had been
anticipating at this stage. If as well as the UK economic system is overheating
greater than different international locations (which is an affordable interpretation of
the inflation numbers), this quantity is an underestimate! (UK GDP is
flattered as a result of it’s unsustainable given persistent inflation.)
In fact this 5% or
extra quantity is admittedly simply our relative efficiency towards chosen
different international locations since 2016, and so it could seize different elements
beside Brexit, reminiscent of dangerous coverage throughout the pandemic, persistent
underfunding of well being companies and heightened
uncertainty as a consequence of political upheaval detering funding.
In fascinated by
the relative positions of combination demand and provide, I didn’t need
to consider that UK provide had been hit a lot and so rapidly since
2016. [4] The proof of persistent inflation means that perception
was wishful considering. It appears the financial penalties of this era of
Conservative authorities for common residing requirements within the UK has
been terribly dangerous.
[1] The UK was additionally
significantly badly
hit by excessive vitality costs.
[2] Within the first
quarter of this yr GDP
per capita isn’t solely beneath 2019 ranges, additionally it is
beneath ranges on the finish of 2017!
[3] Increased curiosity
charges don’t scale back demand solely by lowering some folks’s
incomes. Additionally they encourage corporations and shoppers to substitute future
consumption for present consumption by saving extra and spending much less.
Nonetheless with nominal rates of interest beneath inflation, actual curiosity
charges thus far have been encouraging the other.
[4] I most likely
ought to have identified higher given what occurred following 2010
austerity. Whereas it’s arduous for politicians to considerably elevate
the speed of development of combination provide, some appear to search out it a lot
simpler to cut back it considerably.