On this put up, we consider how deposits have advanced over the latter portion of the present financial coverage tightening cycle. We discover that whereas deposit betas have continued to rise, they didn’t speed up following the financial institution runs in March 2023. As well as, whereas general deposit funding has remained secure, we discover that the banks most affected by the March 2023 occasions are providing increased deposit charges and are rising their deposit funding relative to the broader banking business.
Financial Coverage and Banks’ Safety Losses
The start of 2022 noticed distinctive situations within the banking sector relative to prior cycles. Deposits and reserves had been at their highest ranges because the world monetary disaster (GFC) of 2007-08, whereas coverage charges had been successfully on the zero decrease sure. These situations had been partially attributable to the distinctive nature of the COVID recession and the assorted types of authorities help that sought to reduce disruptions to banks, companies, and households.
The Federal Reserve launched into a speedy tightening cycle in March 2022 to counter a big enhance in inflation. By March 2023, rate of interest will increase had diminished the worth of assorted fixed-rate belongings, like securities and mortgages, leading to substantial unrealized losses within the banking sector. Sometimes, such losses stay unrealized as a result of banks can maintain their fixed-rate belongings to maturity since these are funded by comparatively mounted, long-maturity liabilities (see this April 2023 put up for extra on this phenomenon). On this case, nevertheless, a number of banks skilled depositor flight in response to solvency considerations.
Given these disruptions, there was a threat that pervasive unrealized losses would possibly encourage a revision in depositor habits that may imperil the broader banking system by forcing extra establishments to lift deposit charges or search costly funding to keep away from promoting belongings and realizing interest-rate-related losses.
Business Deposit Situations Seem Steady
The price of deposits relative to prevailing rates of interest has continued to extend, however the tempo of change has appeared secure following the occasions in March 2023. The chart beneath depicts the change in general deposit charges relative to adjustments within the federal funds charges—or the cumulative beta—over the course of the final 5 tightening cycles for the banking business. Since 2023:Q1, the cumulative beta of deposits has continued to rise. Whereas the present tightening cycle now resembles these previous to the GFC, there doesn’t seem to have been a pointy change within the development of deposit pricing following the occasions in March.
Business Deposit Beta Continues to Rise at a Regular Price
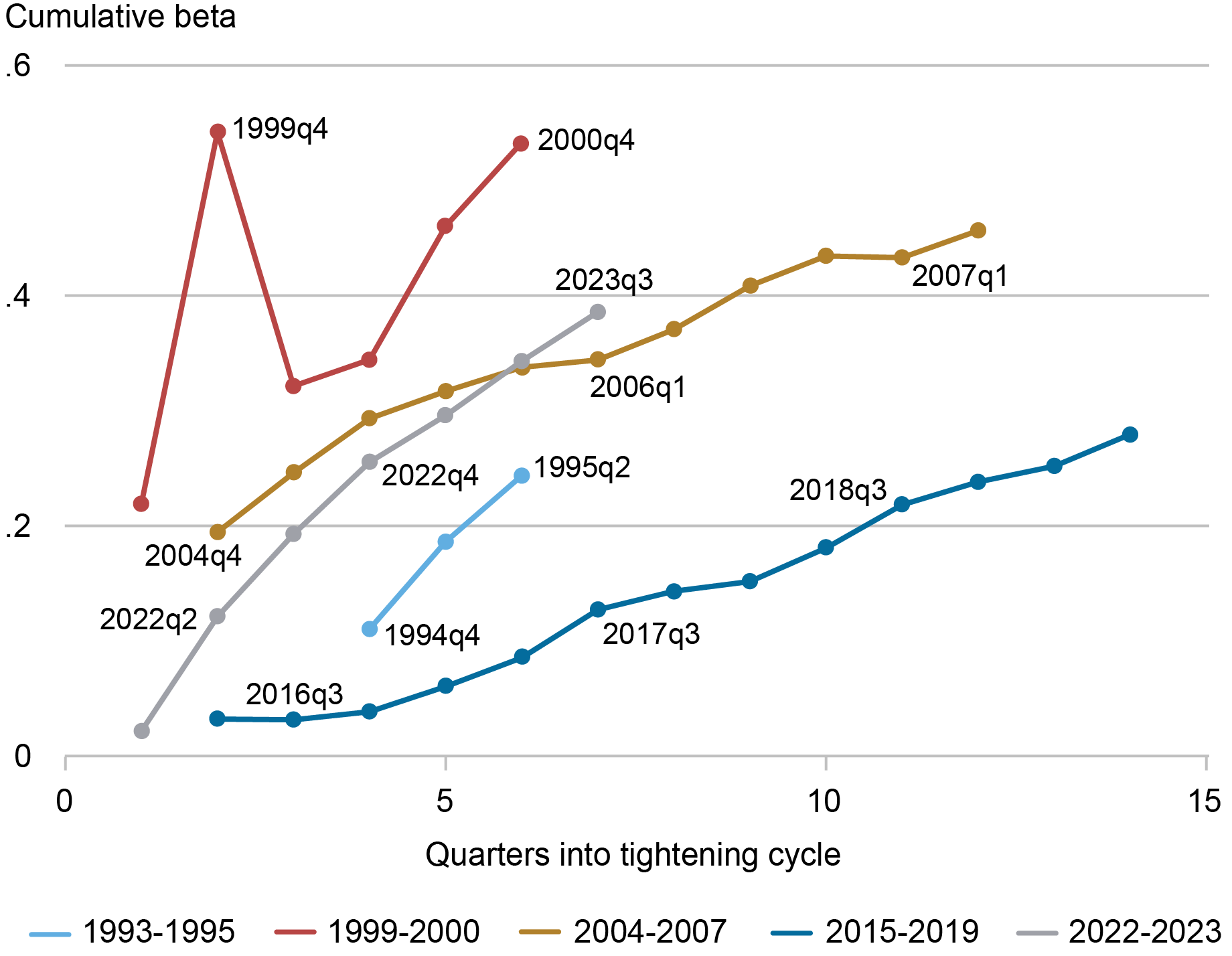
Notes: Betas are the cumulative change of implied deposit charges on complete deposits (interest-bearing and noninterest-bearing) relative to the change within the common quarterly federal funds price. Implied deposit charges are estimated because the curiosity expense on deposits divided by the common deposit steadiness within the quarter.
However, the composition of financial institution funding has continued to evolve. The chart beneath depicts the evolution of sources of business funding relative to complete belongings in 2019:Q2. For this train we keep a balanced panel of banks and exclude the banks that failed in March 2023. This method permits us to review the relative significance of every class of funding in addition to the change in funding over time.
The chart reveals that the business grew considerably through the downturn, with belongings up roughly 30 p.c by means of 2021:This fall relative to 2019:Q2 (the darkish blue line). The expansion in belongings was primarily funded by the expansion in interest-bearing (the sunshine blue line) and noninterest-bearing (the purple line) deposits. Since 2021:This fall, belongings have remained roughly flat: declines in noninterest deposits had been offset by an increase in different debt (the gold line) akin to advances from Federal Residence Mortgage Banks (FHLB) and interest-bearing deposits (together with time deposits). These traits seem unchanged following the occasions of 2023:Q1.
Business Asset Progress Has Slowed, however Total Funding Is Steady
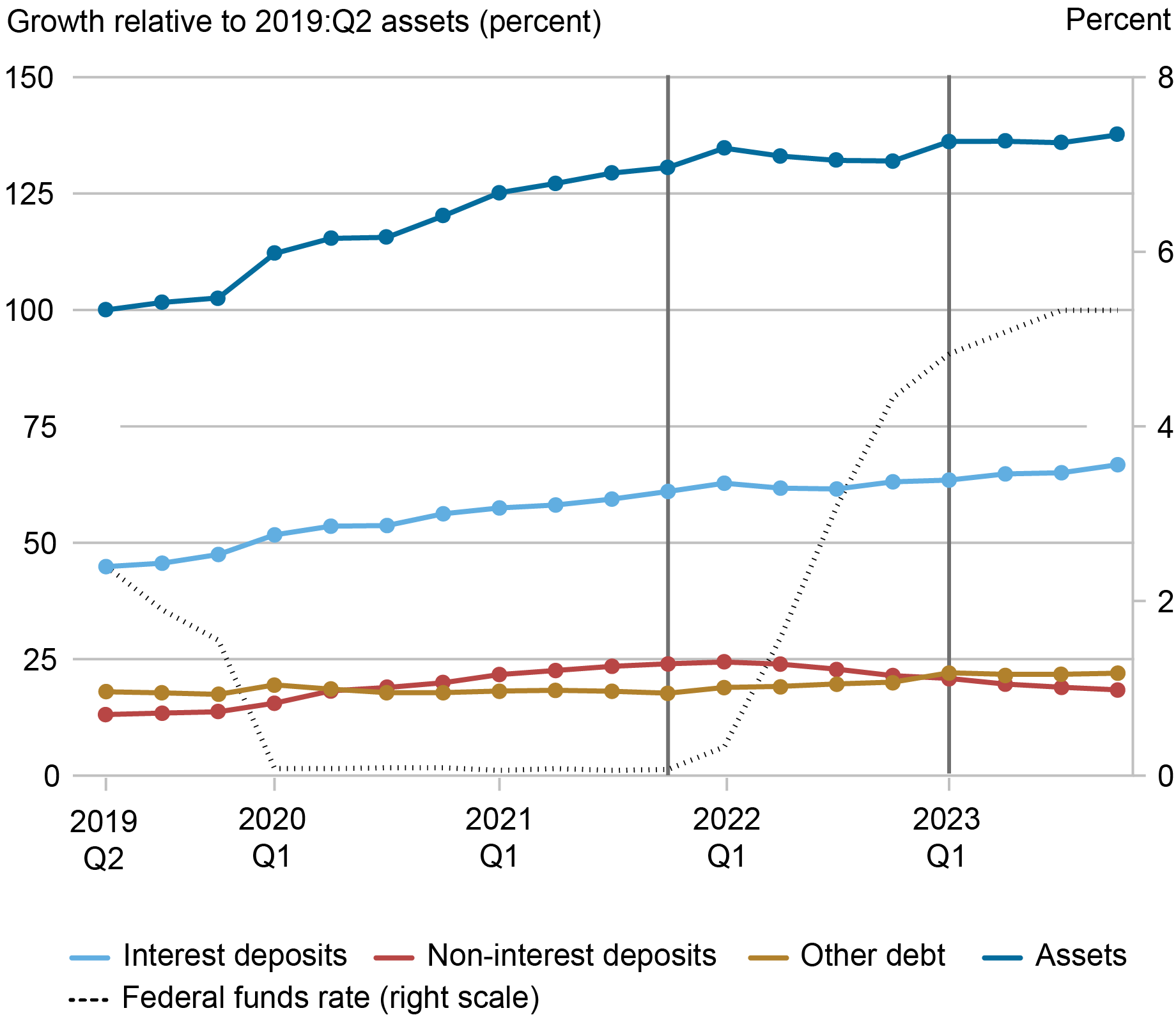
Notes: Business portions are plotted relative to complete belongings in 2019:Q2, which illustrates dynamics over time in addition to their significance relative to the scale of the business. The primary vertical line signifies the beginning of the present tightening cycle; the second signifies the turmoil within the banking sector in March 2023.
Deposit Pricing and Funding throughout Banks
Because the occasions in March, financial institution misery has been concentrated in a subset of banks and never readily noticed on the business degree. Right here we look at how deposit worth and funding situations modified for banks of various sizes. That is notably insightful as a result of a lot of the rapid misery following the occasions in March 2023 was concentrated amongst financial institution holding firms (BHCs) between $50 billion and $250 billion in belongings, often known as “super-regionals” (see this Could 2023 weblog put up). These banks skilled giant deposit outflows that had been principally directed towards the biggest banks (these with belongings of at the very least $250 billion).
The chart beneath illustrates the evolution of cumulative deposit betas through the present tightening cycle throughout the distribution of financial institution dimension. There are significant variations within the cumulative deposit betas, with super-regionals (the gold line) being a key outlier. Deposit betas for these establishments have usually been increased than these of smaller banks all through this tightening cycle. Nonetheless, the distinction with smaller banks emerged previous to 2023:Q1 and remained constant by means of the March episode. Certainly, there don’t seem to have been significant shifts within the betas of super-regionals relative to these of smaller banks because the financial institution run.
For the biggest banks, betas have been going up at a slower tempo than these of different banks. This will replicate the perceived security of those establishments relative to different banks and is in step with the move of deposits to the biggest banks across the Silicon Valley Financial institution episode.
Tremendous-Regionals Exhibit Persistently Larger Deposit Betas
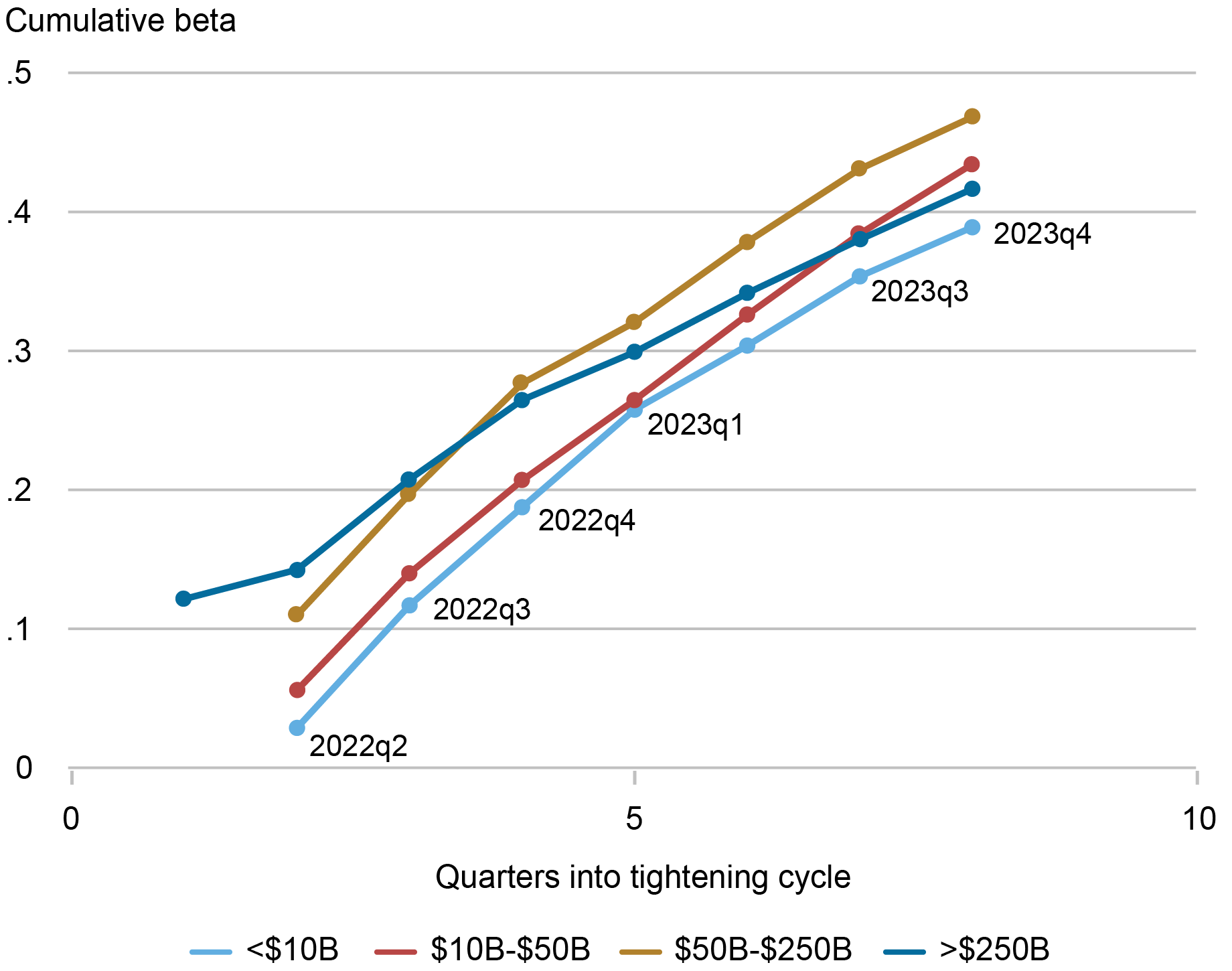
Sources: FR Y-9C information; authors’ calculations.
Notes: Betas are the cumulative change of implied deposit charges on complete deposits (interest-bearing and noninterest-bearing) relative to the change within the common quarterly federal funds price. Implied deposit charges are estimated because the curiosity expense on deposits divided by the common deposit steadiness within the quarter. BHCs are positioned in dimension buckets utilizing asset dimension in 2009:This fall {dollars}.
Turning to balances, super-regionals have additionally skilled differential funding patterns relative to the business as an entire. The chart beneath summarizes the relative significance of every funding class together with the evolution since 2019:Q2. For the super-regionals, belongings grew consistent with the business as much as the quarter during which charges elevated. Nonetheless, after charges started to rise, the super-regionals continued to develop whereas the business has remained roughly flat. The expansion in super-regional BHCs displays the continued enhance in interest-bearing deposits and, to a lesser diploma, different debt. In affiliation with super-regionals’ higher responsiveness to rates of interest, these outcomes counsel that these banks have raised their charges by extra however have additionally been in a position to develop interest-bearing deposits relative to the business.
Tremendous-Regional Asset and Deposit Progress Exceeds the Business
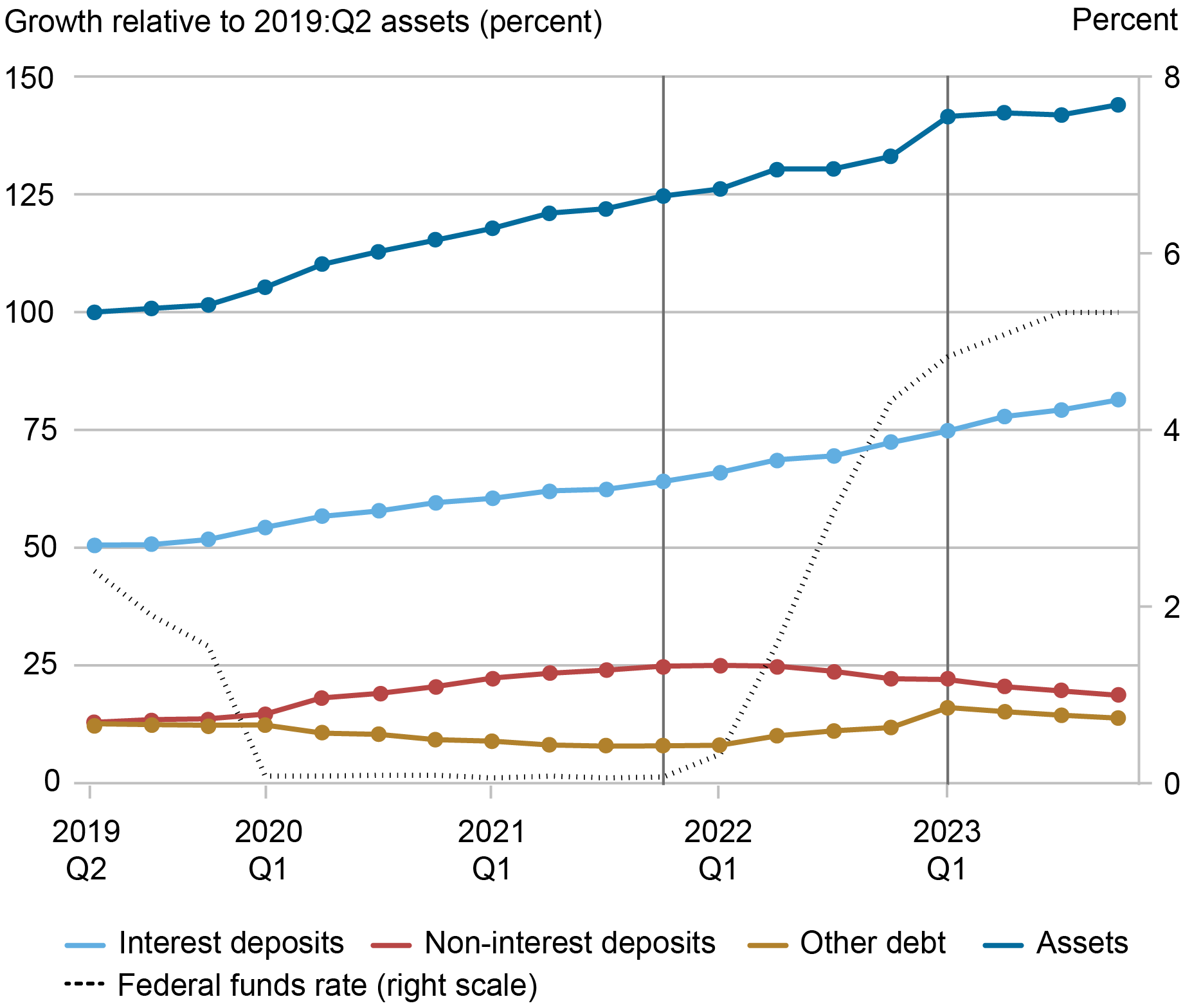
Sources: FR Y-9C information; authors’ calculations.
Notes: Business portions are plotted relative to complete belongings in 2019:Q2, which illustrates dynamics over time in addition to their significance relative to the scale of the business. The primary vertical line signifies the beginning of the present tightening cycle; the second signifies the turmoil within the banking sector in March 2023.
Summing Up
The occasions of March 2023 elevated the saliency of the sensitivity of deposit funding to macroeconomic and bank-specific situations. Our assessment of deposit pricing and funding since that point signifies that the business seems to have prevented a big change in depositor habits that may additional stress earnings and capital. This will partially have been because of authorities interventions, such because the ensures prolonged to depositors and creation of the Financial institution Time period Funding Facility.
Additional, we doc that the deposit pricing of super-regional banks has exhibited a higher sensitivity to rising charges. In keeping with increased charges, these banks have additionally grown deposit funding relative to the broader banking business. In our subsequent put up, we’ll discover the long run path of deposit charges given the present impartial stance of financial coverage.

Stephan Luck is a monetary analysis advisor in Banking Research within the Federal Reserve Financial institution of New York’s Analysis and Statistics Group.

Matthew Plosser is a monetary analysis advisor in Banking Research within the Federal Reserve Financial institution of New York’s Analysis and Statistics Group.
How one can cite this put up:
Stephan Luck and Matthew Plosser, “Deposits and the March 2023 Banking Disaster—A Retrospective,” Federal Reserve Financial institution of New York Liberty Avenue Economics, March 27, 2024, https://libertystreeteconomics.newyorkfed.org/2024/03/deposits-and-the-march-2023-banking-crisis-a-retrospective/.
Disclaimer
The views expressed on this put up are these of the writer(s) and don’t essentially replicate the place of the Federal Reserve Financial institution of New York or the Federal Reserve System. Any errors or omissions are the accountability of the writer(s).

